Use Agentic AI to generate smarter API tests. In minutes. Learn how >>
Jump to Section
How Is the Test Automation Pyramid Used in Software Development?
Here is a thorough discussion on how the testing automation pyramid can be deployed in software development and the solutions Parasoft provides for each phase of the testing pyramid.
Jump to Section
Jump to Section
The test automation pyramid, created by Mike Cohn and popularized by Martin Fowler, has changed the way we think of software testing. It guides what types of tests to perform and how many of each type of test to perform. The testing automation pyramid has helped create more efficient testing and resulted in more reliable software being released to customers.
Benefits of the Testing Automation Pyramid
Most of the benefits of test automation are obvious:
- Cost and time savings.
- Better accuracy eliminating human error.
- Ability to repeat, reuse, and scale tests to your software needs.
But why is the testing automation pyramid so important in automated software testing?
Just automation alone will not get you where you want to go in software development that’s on a tight timeline and budget. There will still be limited resources and limited time.
How can we design the appropriate types of automated tests at the correct volume in order to scale up testing with development practices? The test pyramid is a great guide to do just that!
Below is an overview of the testing pyramid and how each phase of the pyramid is used in software development.
Traversing the Testing Automation Pyramid
The testing pyramid is a great visual metaphor describing different testing layers and how much testing to do in each layer.
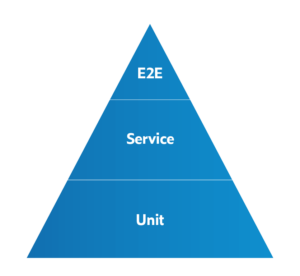
Unit tests are on the bottom and represent the most granular tests, of which you should have many.
The next layer up in the pyramid has service layer or integration tests. This is where you begin testing how your software components interact with one another whether those are internal or external integrations.
The end-to-end test (E2E) is the most complex and tests the software as a whole to ensure it works as expected from start to finish.
Keeping the volume of your test suites in each layer aligned to this visual metaphor of a pyramid lets you scale up testing to result in more reliable software. Let’s dig into why.
Unit Tests
A unit test is performed on a small portion of code, typically a function/method or up to a class, to determine if it fulfills its function correctly. The characteristics of these tests are simple and fast, which is why you want a large percentage of your tests in this layer. When a unit test fails, developers are alerted and can quickly ascertain what the unintended consequences of their code changes are, and this serves as a critical safety net for changing the code with confidence.
For all their advantages, unit tests are not the end-all-be-all of testing. With such narrowly scoped tests that use test doubles (such as mocks and stubs), you lose verification of how large portions of the software work together.
If you’re interested in verifying business requirements, that’s difficult to facilitate with unit tests, and as the expression goes, “you can’t see the forest for the trees.” However, a policy of mapping and tracking unit tests to user stories as they’re worked on can serve to help identify risks associated to certain features when you see instability in unit tests failing.
How Parasoft Helps With Unit Testing
Parasoft C/C++test detects defects early and saves money by integrating C and C++ testing into the development of software for embedded safety- and security-critical applications.
Parasoft Jtest integrates tightly into your development ecosystem and CI/CD pipeline for real-time, intelligent feedback on your Java testing and compliance progress. Jtest highlights code coverage, employs deep code analysis to assist with JUnit creation, and identifies security and reliability issues so stakeholders can understand the quality of the deliverables and make informed decisions about risk of release.
Integration Tests
Integration testing is the middle tier of the standard test pyramid. Where unit tests are very granular, at this level we utilize tests that start verifying that larger packages of code function correctly together.
Integration testing is more important now than ever due to the popularity of distributed system architectures with microservices and cloud deployments. The days of developing monolithic applications are long past and many modern systems’ independently deployed software components integrate with one another through their exposed interfaces, often via REST or a message broker like Apache Kafka or ActiveMQ. Legacy systems are slowly getting decoupled and broken apart into new software components that are easier to scale and easier to test, despite being a more complex deployment.
Fitch Delivers High Code Coverage & Quality for Microservices Applications
These tests are slower to run than unit tests and require your software to be deployed in a test environment, but they can catch tricky problems that unit tests miss. And they’re crucial to testing your software efficiently when compared to end-to-end or system-level tests.
Due to the nature of a larger testing scope, the time to diagnose and remediate issues increases. However, as with unit tests, integration tests can be repeated until all tests are successful and the build pipeline is ready to move into (or back into) end-to-end testing, covered below.
In software development today, integration tests are a very under tested area as it can be seen as the “middle ground” between development testing and QA testing. Fingers can get pointed about who should test this layer (spoiler alert… the answer is BOTH). It takes a very tech savvy tester with the appropriate tools to perform integration testing correctly.
How Parasoft Helps With Integration Testing
Parasoft SOAtest delivers fully integrated API and web service testing tools that automate functional and nonfunctional API testing. Teams can streamline automated testing with advanced codeless test creation capabilities for applications with multiple interfaces (REST and SOAP APIs, microservices, reactive architectures, databases, legacy systems, and more).
The tools reduce the risk of security breaches and performance outages by transforming functional testing artifacts into security and load equivalents. Smart test execution facilitated by a binary diff analysis of changes in the packaged software between builds ensures intra-day builds test what needs testing while skipping the rest. Such optimizations and reuse, along with continuous monitoring of APIs for change, allows faster and more efficient testing.
Parasoft Virtualize goes beyond basic mocking and stubbing to create a more robust simulation environment for APIs and services. It deploys a “digital twin” of your test environment to use as a sandbox for partner development or as a virtual endpoint for internal testing.
Virtualize enables testers and developers to simulate services or data when access is limited or unreliable. Adopting service virtualization also results in direct infrastructure cost savings while the scope of test automation grows. The results can be easily integrated with other testing practices and visualized for faster failure detection and debugging with an intuitive codeless interface.
Create, Deploy, & Manage Virtual Test Environments With Parasoft Virtualize
End-to-End Tests
End-to-end testing tests the largest amount of code (as in the entire software application, from end to end). They use data and a test environment to simulate real-world operation of the software. It is the most expensive to maintain and the slowest to run. Since this tests fully assembled applications, it’s also the hardest phase of testing in which to diagnose problems (yikes).
But it’s the easiest to design since it follows business requirements of the software. A less technical business analyst or product owner could define what these tests should do. This may partly explain the popularity of BDD practices in test automation.
As organizations mature their software development process and start automating tests, many fall into a trap where most of their tests fall into this category. Eventually, they hit a bottleneck.
Development is adopting Agile and DevOps practices, and speeding up. Yet testing is always behind, missing testing of new features. And testing generally has a hobbled impact on catching software quality issues as the pace of development increases. This is why the test pyramid is so valuable as teams modernize.
You can’t keep up without automation. More importantly, you can’t keep up unless you have a solid blueprint that shows you how you should be testing. This is where organizations begin to value “lean UI testing” as a mantra, as they see first-hand how their testing strategy can no longer scale with the pace of development.
If you see your organization trapped in this paradigm, begin seeking opportunities to refactor functional tests down from the UI layer to the service layer. Keep UI tests focused on testing client-side logic, user journey, critical paths, and cross-platform certification.
How Parasoft Helps With End-to-End Testing
Parasoft Selenic is a lightweight addition for Selenium testers that applies machine learning to automatically heal unstable or stale tests suffering from constantly changing HTML DOMs and unpredictable response times.
Run your Selenium UI tests with confidence, knowing that Selenic’s self-healing capability with enhanced locator and wait condition strategies will detect unstable tests, recover from them on the fly during execution, and enable IDE quick-fix workflows to reduce the maintenance burden of your UI tests. Selenic also provides a Chrome extension to record UI actions and generate Selenium WebDriver code in Java that follows the Selenium best practice page object model pattern.
Parasoft Testing Pyramid
While the test automation pyramid provides a blueprint for an efficient test automation strategy, you cannot test quality into an application. The pyramid needs to be built on a solid foundation of deep code analysis focused on identifying and preventing reliability and security issues. The Parasoft testing pyramid shows how Parasoft’s Continuous Quality Testing Platform solutions automate testing across each level.
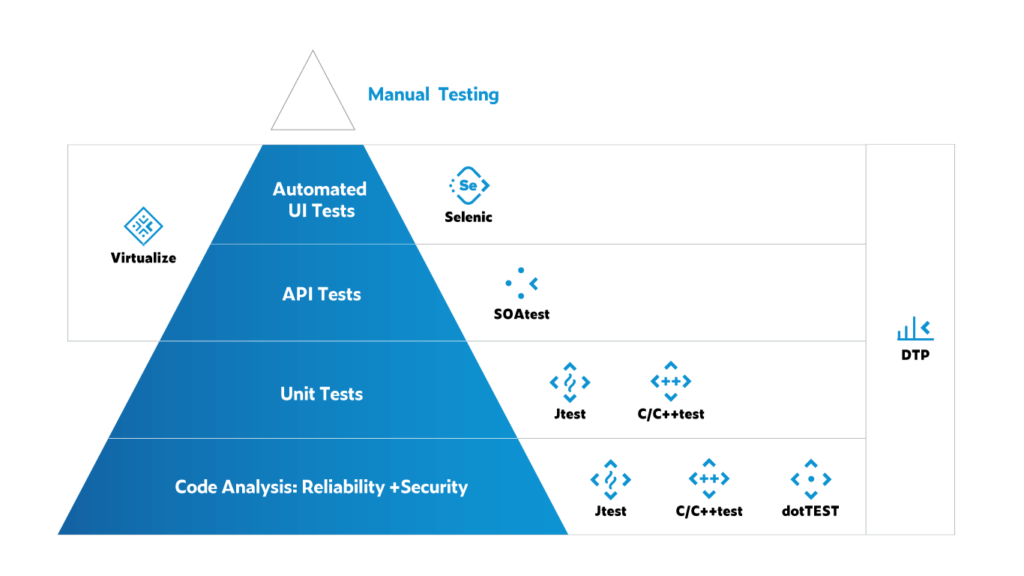
Results across these levels can be consolidated into Parasoft’s reporting, analytics, and compliance dashboard, Parasoft DTP, providing a unified view of software quality and test coverage. Your team gets insights to analyze your application’s status and determine the next steps for reaching your goals.
Parasoft Continuous Quality Testing Platform




